Immunological factors in unexplained implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage

Sex-linked genetic diseases (X-linked)

Single-gene diseases
Single-gene diseases, as the name suggests, occur due to mutations (disease-causing genetic changes) in a specific gene. These diseases often have a specific inheritance pattern and are also known as Mendelian disorders.
Single-gene diseases are divided into two main categories: those with a recessive inheritance pattern, which do not cause symptoms in an individual unless two defective copies of the gene are inherited from both parents, and the second category includes disorders that are called dominant, and for the disease to manifest, only inheritance of one defective copy of the gene from only one parent is needed. Today, a large number of single-gene diseases, resulting from defects in hundreds of different genes, have been identified.
Most of these disorders are rare, however, some of them are relatively common.

Some of the most common recessive autosomal diseases
Beta thalassemia
A type of inherited or genetic anemia that occurs in two forms, mild (minor) and severe (major). Symptoms appear from the age of 6 months onward, including pallor, sleep disturbances, weakness, and lethargy in the child. As the child grows older, other complications of the disease such as widening of the facial bones, changes in the patient’s facial appearance, enlargement of the liver and spleen, and growth disorders also appear.
Cystic fibrosis
A disorder that affects the lungs, pancreas, and other organs, leading to respiratory and digestive problems.
Sickle cell anemia
A blood disorder characterized by abnormal red blood cells that can cause pain, organ damage, and an increased risk of infection.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A disorder that affects the body’s ability to process a specific amino acid, leading to intellectual disability and other health problems.
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
A genetic disorder characterized by weakness and wasting (atrophy) of the muscles used for movement (skeletal muscles). This disease is caused by the loss of specialized nerve cells called motor neurons that control muscle movements.
Albinism
A group of inherited disorders that affect the production of melanin, leading to light-colored skin, hair, and eyes.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
A group of disorders that affect the production of steroid hormones and lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications.
Tay-Sachs disease
A type of genetic disease in children and a rare and fatal neurological disorder that affects infants and young children.
Gaucher's disease
A genetic disorder that causes the buildup of fatty substances in cells and organs, leading to damage to bones and organs.
Hemochromatosis
A disorder that causes the body to absorb too much iron, leading to damage to organs such as the liver and pancreas.
Wilson's disease
A disorder that causes copper to build up in the liver, brain, and other organs, leading to liver disease and neurological problems.
Cystinosis
A rare genetic disease in Iran that causes the buildup of an amino acid called cystine in cells, leading to kidney damage and other health problems.
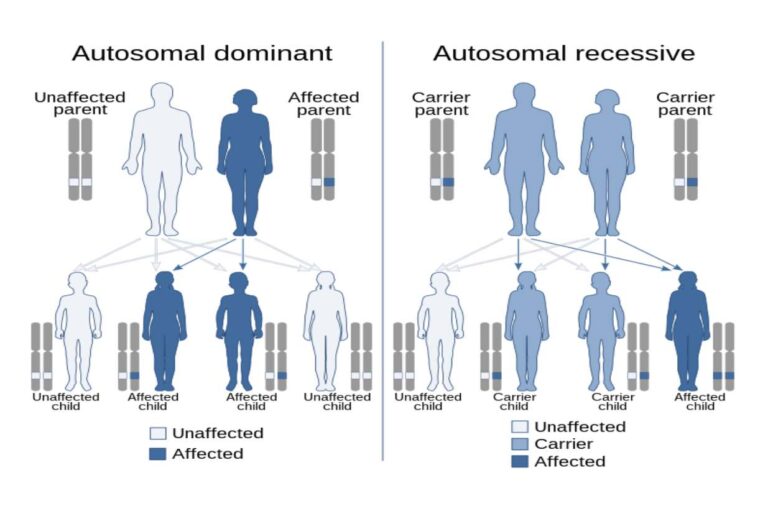
Some of the most common dominant autosomal diseases
Achondroplasia
A bone growth disorder that leads to short stature and abnormalities in the limbs and skull.
Polycystic kidney disease
A disease that causes the growth of many cysts in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage and failure.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
A connective tissue disorder that affects the skin, joints, and blood vessels.
Marfan syndrome
A disorder where connective tissue is abnormal. As a result, various body systems, including the cardiovascular system, bones, tendons, cartilage, eyes, skin, and lungs, are affected.
Huntington's disease
A genetic disease that affects the brain and gets worse over time. The main symptoms of Huntington’s include uncontrollable movements of the limbs and eventually dementia.
Myotonic dystrophy
This disease is one of the hereditary diseases that is classified in the group of muscular dystrophy. Myotonic dystrophy is the most common type of muscular disease that starts in adulthood and affects the individual. This disease is accompanied by progressive muscle wasting and weakness.
Neurofibromatosis
A disorder that causes the growth of tumors on nerves and causes various symptoms and complications.
Hereditary spherocytosis
A blood disorder characterized by abnormally shaped red blood cells and can lead to anemia and jaundice.
Hypercholesterolemia
A familial disorder that causes high levels of cholesterol in the blood and increases the risk of heart disease.
Osteogenesis imperfecta
A condition that causes bones to be brittle and increases the risk of fracture.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
A group of inherited disorders that affect the nerves of the arms and legs, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
The genetics laboratory of the Shiraz Infertility Treatment Center is proud to announce that it has performed the first PGD for three disease-causing genes simultaneously in a couple in Iran, using the most advanced technologies and the latest modern laboratory equipment, and is ready to provide all PGD services for the aforementioned diseases to dear clients.

