Introduction to the Embryology Department
Shiraz Fertility Center
The embryology department at Shiraz Fertility Center, equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and staffed by the best specialists, has brought joy to countless families.
Headed by Dr. Shirzad Hosseini, a specialist in embryology, the department oversees all procedures related to embryo transfer.
The embryology department is divided into four sub-sections
Procedures in the Embryology Department
Essential guidelines for preparing a semen or sperm sample
1-Abstain from ejaculation for 2-3 days prior to egg retrieval.
2-Get adequate rest and a nutritious meal the night before the procedure.
3-Be present at the center on the morning of the egg retrieval procedure to provide a sperm sample.
4-The sample container must be labeled by the center’s reception desk. Containers brought from outside the center are not acceptable.
5-Do not use any lubricants, water, or other substances when providing the sample as these can damage the sperm.
6-If you have a fever, are taking any medications, or have used any illicit drugs, please inform the embryology department.
7-Even if you have frozen sperm, a fresh sample is still required as fresh sperm is preferred.
8-If you encounter any difficulties providing the sample, please inform the embryology department immediately for further guidance.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Following egg retrieval, the collected follicles are transferred to the embryology laboratory. Embryologists isolate the eggs from the follicular fluid, wash them, and remove any surrounding cells to prepare them for sperm injection. Concurrently, the andrology laboratory prepares the sperm for injection using specific protocols.
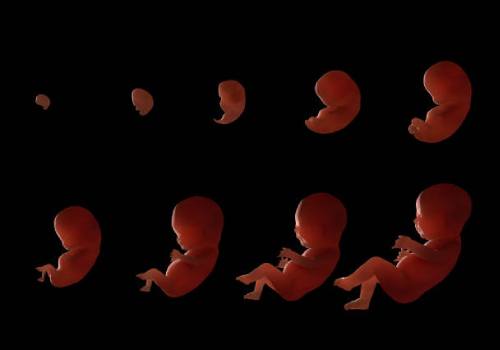
An embryologist injects a single sperm into each egg using an extremely fine needle under a microscope. After the injection, the eggs are transferred to a special culture dish and placed in an incubator, which simulates the conditions of a woman’s uterus in terms of temperature, oxygen, and CO2 levels.The following day, an embryologist assesses the fertilization rate of the eggs, changes the culture medium, and based on the patient’s treatment plan and the physician’s recommendation, either freezes the embryos or transfers them to the mother’s uterus in the subsequent days.
Regarding embryo development, it’s important to note that:
1- The number of eggs retrieved during egg retrieval does not always match the number of follicles seen on ultrasound.
2- Not all eggs retrieved on the day of egg retrieval are mature and suitable for injection. Some may be immature or dark in color, reducing the total number of eggs available for fertilization.
3- Approximately 70% of injected eggs are successfully fertilized and develop into embryos. However, this percentage can vary depending on the quality of the eggs and sperm. Therefore, the number of embryos is often less than the number of eggs.
4- Embryo development may cease at any stage. Only embryos of suitable quality for freezing are preserved, resulting in a smaller number of frozen embryos compared to the total number of embryos.
5- If you wish to undergo another egg retrieval due to a low number of embryos or no embryos, please visit the clinic on the first day of your second menstrual cycle following the previous egg retrieval.
Fresh Embryo Transfer
If, based on the doctor’s recommendation and the patient’s condition, it is decided to perform a fresh embryo transfer, the patient will receive information about the medications to be taken and subsequent follow-up ultrasound appointments after egg retrieval. Once the ultrasound confirms that the patient’s uterus is ready for transfer, the patient will be informed of the transfer date.
Embryo Freezing and Subsequent Transfer
In this procedure, after egg retrieval and embryo formation, all embryos are frozen based on the patient’s condition and the doctor’s recommendation. The patient should visit the clinic’s reception between 10 AM and 12 PM, from Saturday to Thursday, two weeks to one month after the egg retrieval to sign the embryo freezing contract. If you decide to proceed with an embryo transfer in consultation with your doctor, please visit the clinic between the 12th and 14th day of your second menstrual cycle with the signed freezing contract (in the afternoon) to receive a prescription for medications to prepare the uterine lining for embryo transfer and to schedule the transfer date.
Pre-Embryo Transfer Procedures
1-Studies have shown that lower stress levels increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Therefore, maintaining emotional and mental calmness and avoiding stressful situations is recommended.
2-For breakfast on the day of transfer, you can have sweet tea with honey or pulp-free juice. (Milk is not allowed.)
3-Be present at the center at the scheduled time on the day of transfer with a semi-full bladder.
4-Embryo transfer is typically performed on day 5 if PGD is performed, and on day 3 or 5 in normal cases, depending on the number and quality of embryos and the decision of the embryology department.
5-The number of embryos transferred to the patient is based on the patient’s age and the quality of the embryos, in accordance with the latest global standards.
Embryo Transfer Process
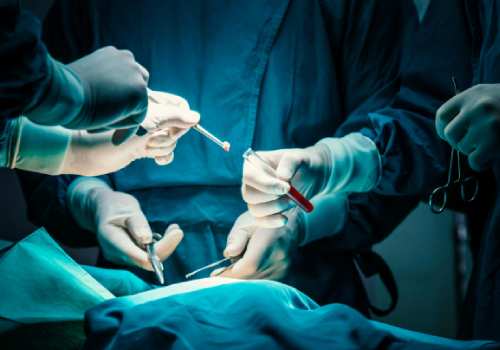
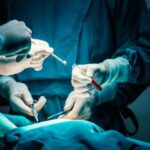
The embryologist selects the predetermined number of embryos based on the patient’s age and embryo quality using a syringe attached to a catheter. The embryos are then injected into the uterus through another catheter that the doctor places inside the uterus, guided by ultrasound.
Post-Embryo Transfer Procedures
1- Complete bed rest is not necessary after embryo transfer. Excessive rest and constant lying down can decrease the chances of a successful pregnancy. Rest for 24 hours and then resume your normal daily routine as in a natural pregnancy.
2- Avoid heavy exercise and lifting heavy objects. Light walking and exercise are fine.
3- Avoid sexual intercourse until the pregnancy result is known.
4- Avoid hot baths, swimming pools, and vaginal douches.
5- Avoid smoking, hookah, alcoholic beverages, caffeinated drinks, unhealthy foods containing preservatives, and foods that cause constipation or bloating.
6- Consume fresh fruits and vegetables, protein-rich foods, and carbohydrates.
7- You may experience slight spotting or bleeding after the embryo transfer, which is not a cause for concern. However, contact your doctor if you have any doubts or concerns.
8- Take a pregnancy test (blood test) three weeks after the embryo transfer.
9- If the test is positive, visit the clinic for an ultrasound six weeks after the embryo transfer.
10- If the test is negative, continue the medications for three days and then take another test. If the second test is also negative, stop taking the medications.
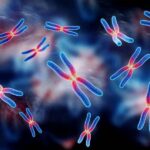
Embryo Biopsy for Sex Determination and Chromosome 13, 18, 21 Screening
In this procedure, the embryologist first assesses the quality and suitability of the embryos for biopsy. High-quality 3-day-old embryos are selected, and a single cell is removed using a laser for chromosomal analysis and sex determination. The biopsied cell is then sent to the genetics laboratory, and the biopsied embryos are cultured separately until the genetic results are available.
Important Notes on Embryo Biopsy for Sex Determination and Chromosome 13, 18, 21 Screening
1- If the embryo is of good quality, the biopsy process, which involves removing a cell from an 8-cell embryo, does not harm the embryo’s organs. In the worst-case scenario, it may prevent the 3-day-old embryo from developing further.
2- The sex and chromosomal status of each embryo for chromosomes 13, 18, and 21 will be reported by the genetics laboratory to the patient and embryology department on the morning of the transfer.
3- The final number of embryos suitable for biopsy may be lower than the initial number due to poor embryo quality, failure to develop, or failure to recover from freezing.
4- In some cases, for the reasons stated below, there may be no embryos available for transfer after genetic testing:
– The embryo may be chromosomally normal but not of the desired sex.
– The embryo may be of the desired sex but have a genetic abnormality on chromosomes 13, 18, or 21, making it unsuitable for transfer.
– The embryo may be of the desired sex but its growth may have stopped in culture, making it unsuitable for transfer.
5- Since genetic testing involves the use of genetic kits and many other consumables, there is no refund if no healthy embryos are available for transfer.
Embryo Biopsy for Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) is divided into two types:
1- Array CGH test: This test is used to analyze the number of all chromosomes.
2- Single-gene diagnosis test: This test is used to detect mutations in a specific gene. In this method, all embryos are cultured in vitro until day 5. Once they reach the biopsy stage, 4-8 cells are individually biopsied from each embryo and sent to the genetics laboratory for analysis. The corresponding embryo is then frozen until the genetic results are ready.
After genetic testing and the results are ready, the patient will be contacted to arrange for embryo transfer.
Important Notes on Embryo Biopsy for Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
1- Approximately 40% of cultured embryos reach a stage where they can be biopsied. (It’s important to note that embryos that don’t reach day 5 lack the necessary quality for continued growth.)
2- After biopsy, embryos are frozen, and samples are sent to the genetics laboratory for analysis.
3- It is possible that after array CGH analysis, none of the embryos will have a balanced chromosome number, or that no normal embryos will be found when screening for a specific disease (molecular PGD), resulting in a canceled transfer.
4- According to the genetics report, an embryo may be genetically and chromosomally healthy, but it may not be suitable for transfer after thawing due to poor quality.
5- Due to the use of genetic kits and numerous consumables in the array CGH and molecular testing processes, no refunds will be provided if there are no healthy embryos available for transfer.
1-Abstain from ejaculation for 2-3 days prior to egg retrieval.
2-Get adequate rest and a nutritious meal the night before the procedure.
3-Be present at the center on the morning of the egg retrieval procedure to provide a sperm sample.
4-The sample container must be labeled by the center's reception desk. Containers brought from outside the center are not acceptable.
5-Do not use any lubricants, water, or other substances when providing the sample as these can damage the sperm.
6-If you have a fever, are taking any medications, or have used any illicit drugs, please inform the embryology department.
7-Even if you have frozen sperm, a fresh sample is still required as fresh sperm is preferred.
8-If you encounter any difficulties providing the sample, please inform the embryology department immediately for further guidance.
Following egg retrieval, the collected follicles are transferred to the embryology laboratory. Embryologists isolate the eggs from the follicular fluid, wash them, and remove any surrounding cells to prepare them for sperm injection. Concurrently, the andrology laboratory prepares the sperm for injection using specific protocols.
An embryologist injects a single sperm into each egg using an extremely fine needle under a microscope. After the injection, the eggs are transferred to a special culture dish and placed in an incubator, which simulates the conditions of a woman's uterus in terms of temperature, oxygen, and CO2 levels.The following day, an embryologist assesses the fertilization rate of the eggs, changes the culture medium, and based on the patient's treatment plan and the physician's recommendation, either freezes the embryos or transfers them to the mother's uterus in the subsequent days.
Regarding embryo development, it's important to note that:
1- The number of eggs retrieved during egg retrieval does not always match the number of follicles seen on ultrasound.
2- Not all eggs retrieved on the day of egg retrieval are mature and suitable for injection. Some may be immature or dark in color, reducing the total number of eggs available for fertilization.
3- Approximately 70% of injected eggs are successfully fertilized and develop into embryos. However, this percentage can vary depending on the quality of the eggs and sperm. Therefore, the number of embryos is often less than the number of eggs.
4- Embryo development may cease at any stage. Only embryos of suitable quality for freezing are preserved, resulting in a smaller number of frozen embryos compared to the total number of embryos.
5- If you wish to undergo another egg retrieval due to a low number of embryos or no embryos, please visit the clinic on the first day of your second menstrual cycle following the previous egg retrieval.
If, based on the doctor's recommendation and the patient's condition, it is decided to perform a fresh embryo transfer, the patient will receive information about the medications to be taken and subsequent follow-up ultrasound appointments after egg retrieval. Once the ultrasound confirms that the patient's uterus is ready for transfer, the patient will be informed of the transfer date.
In this procedure, after egg retrieval and embryo formation, all embryos are frozen based on the patient's condition and the doctor's recommendation. The patient should visit the clinic's reception between 10 AM and 12 PM, from Saturday to Thursday, two weeks to one month after the egg retrieval to sign the embryo freezing contract. If you decide to proceed with an embryo transfer in consultation with your doctor, please visit the clinic between the 12th and 14th day of your second menstrual cycle with the signed freezing contract (in the afternoon) to receive a prescription for medications to prepare the uterine lining for embryo transfer and to schedule the transfer date.
1-Studies have shown that lower stress levels increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Therefore, maintaining emotional and mental calmness and avoiding stressful situations is recommended.
2-For breakfast on the day of transfer, you can have sweet tea with honey or pulp-free juice. (Milk is not allowed.)
3-Be present at the center at the scheduled time on the day of transfer with a semi-full bladder.
4-Embryo transfer is typically performed on day 5 if PGD is performed, and on day 3 or 5 in normal cases, depending on the number and quality of embryos and the decision of the embryology department.
5-The number of embryos transferred to the patient is based on the patient's age and the quality of the embryos, in accordance with the latest global standards.
The embryologist selects the predetermined number of embryos based on the patient's age and embryo quality using a syringe attached to a catheter. The embryos are then injected into the uterus through another catheter that the doctor places inside the uterus, guided by ultrasound.
1- Complete bed rest is not necessary after embryo transfer. Excessive rest and constant lying down can decrease the chances of a successful pregnancy. Rest for 24 hours and then resume your normal daily routine as in a natural pregnancy.
2- Avoid heavy exercise and lifting heavy objects. Light walking and exercise are fine.
3- Avoid sexual intercourse until the pregnancy result is known.
4- Avoid hot baths, swimming pools, and vaginal douches.
5- Avoid smoking, hookah, alcoholic beverages, caffeinated drinks, unhealthy foods containing preservatives, and foods that cause constipation or bloating.
6- Consume fresh fruits and vegetables, protein-rich foods, and carbohydrates.
7- You may experience slight spotting or bleeding after the embryo transfer, which is not a cause for concern. However, contact your doctor if you have any doubts or concerns.
8- Take a pregnancy test (blood test) three weeks after the embryo transfer.
9- If the test is positive, visit the clinic for an ultrasound six weeks after the embryo transfer.
10- If the test is negative, continue the medications for three days and then take another test. If the second test is also negative, stop taking the medications.
In this procedure, the embryologist first assesses the quality and suitability of the embryos for biopsy. High-quality 3-day-old embryos are selected, and a single cell is removed using a laser for chromosomal analysis and sex determination. The biopsied cell is then sent to the genetics laboratory, and the biopsied embryos are cultured separately until the genetic results are available.
1- If the embryo is of good quality, the biopsy process, which involves removing a cell from an 8-cell embryo, does not harm the embryo's organs. In the worst-case scenario, it may prevent the 3-day-old embryo from developing further.
2- The sex and chromosomal status of each embryo for chromosomes 13, 18, and 21 will be reported by the genetics laboratory to the patient and embryology department on the morning of the transfer.
3- The final number of embryos suitable for biopsy may be lower than the initial number due to poor embryo quality, failure to develop, or failure to recover from freezing.
4- In some cases, for the reasons stated below, there may be no embryos available for transfer after genetic testing:
- The embryo may be chromosomally normal but not of the desired sex.
- The embryo may be of the desired sex but have a genetic abnormality on chromosomes 13, 18, or 21, making it unsuitable for transfer.
- The embryo may be of the desired sex but its growth may have stopped in culture, making it unsuitable for transfer.
5- Since genetic testing involves the use of genetic kits and many other consumables, there is no refund if no healthy embryos are available for transfer.
1- Array CGH test: This test is used to analyze the number of all chromosomes.
2- Single-gene diagnosis test: This test is used to detect mutations in a specific gene. In this method, all embryos are cultured in vitro until day 5. Once they reach the biopsy stage, 4-8 cells are individually biopsied from each embryo and sent to the genetics laboratory for analysis. The corresponding embryo is then frozen until the genetic results are ready.
After genetic testing and the results are ready, the patient will be contacted to arrange for embryo transfer.
1- Approximately 40% of cultured embryos reach a stage where they can be biopsied. (It's important to note that embryos that don't reach day 5 lack the necessary quality for continued growth.)
2- After biopsy, embryos are frozen, and samples are sent to the genetics laboratory for analysis.
3- It is possible that after array CGH analysis, none of the embryos will have a balanced chromosome number, or that no normal embryos will be found when screening for a specific disease (molecular PGD), resulting in a canceled transfer.
4- According to the genetics report, an embryo may be genetically and chromosomally healthy, but it may not be suitable for transfer after thawing due to poor quality.
5- Due to the use of genetic kits and numerous consumables in the array CGH and molecular testing processes, no refunds will be provided if there are no healthy embryos available for transfer.
For more information on embryology, please refer to the following articles.
Polycystic ovary syndrome and ART
Immunological factors in recurrent implantation failure and unexplained miscarriage